Your Cart is Empty
TALK TO AN EXPERT: 1-844-945-3625
Menu
-
- Water Filter Systems
- Portable Solar Generators
- Propane Wall Heaters
- Composting Toilets
- DIY Buildings & Kits
- Canvas Tents
- Homestead & Off Grid Supplies
- Chicken Coops
- Harvest Right Freeze Dryers
- Emergency Food Kits
- Hunting Blinds
- MrCool DIY Mini Splits
- Solar Air Conditioners
- Solar Fridge & Freezers
- Camping Coolers
- Electric Coolers
- Overlanding Gear
- Two Person Cots
- Portable Sauna Tents
- Incinerating Toilets
- Dairy Equipment
- Coolers
- Faraday Defense
- EMP Shield
- Hunting Blinds
- Compost Tumblers
- Drip Irrigation Kits
- Shade Cloth
- Propane Fireplace
- Portable BBQ's
- Brands
- Chicken Coop Brands
- Composting Toilet Brands
- Solar Brands
- Food Storage Brands
- Freeze Dryer Brands
- Water Filtration Brands
- Incinerating Toilet
- Waterless Toilet Brands
- Heater Brands
- EMP Shield Brands
- Tent Brands
- Cot Brands
- Cooler Brands
- Dog Kennels
- Greenhouse & Gazebo Brands
- Portable Saunas
- DIY Shed Kits
- About Wild Oak Trail
- Resource Center
- The Ultimate Prepper & Emergency Survival Blog - Includes Free eBook
- Beginners Guide to Living off The Grid - Includes Free eBook
- Building Your Own Emergency Food Supply
- Best Survival Food to Be Prepared for Anything
- Berkey Lab Tests & Certifications
- Federal Solar Tax Credit - What You Need to Know
- BLOG
-
- 1-844-945-3625
- Login
TALK TO AN EXPERT: 1-844-945-3625
How Do Incinerator Toilets Work?
by Patricia Turla 4 min read
In a remote cabin in the woods, a boat floating serenely on a lake, or an RV parked in the middle of nowhere, the conveniences of city life are distant memories, particularly when it comes to sanitation. For those seeking an eco-friendly and efficient waste management solution, incinerator toilets are increasingly becoming the go-to option.
These innovative systems address waste disposal and offer a sustainable way to maintain hygiene without relying on water or traditional sewage systems. Learn how incinerator toilets work.
Key Takeaways
Incinerator toilets burn human waste at high temperatures, turning it into sterile ash without water. These toilets offer excellent sanitation and space efficiency but require an external power source and have higher upfront costs. Regular maintenance, such as checking the incineration chamber and disposing of ash, ensures optimal performance.
What Are Incinerating Toilets?
Incinerating toilets are an ingenious alternative to traditional toilets. Unlike standard toilets that use water to flush waste into a septic system or sewage network, incinerating toilets rely on high temperatures to burn waste, transforming it into sterile ashes. This process involves collecting solid waste in a specially designed incineration chamber, which undergoes a burn cycle that reduces it to a minimal amount of sterile ash.
The core principle behind incinerating toilets is waste incineration. When human waste enters the incineration chamber, it is exposed to high temperatures, often exceeding 1,000°F (540°C).
These temperatures are achieved using various power sources, such as electricity, natural gas, propane, or diesel. The result is a small amount of ash that is entirely sterile and can be easily disposed of, making incinerating toilets an excellent choice for remote and water-scarce areas.
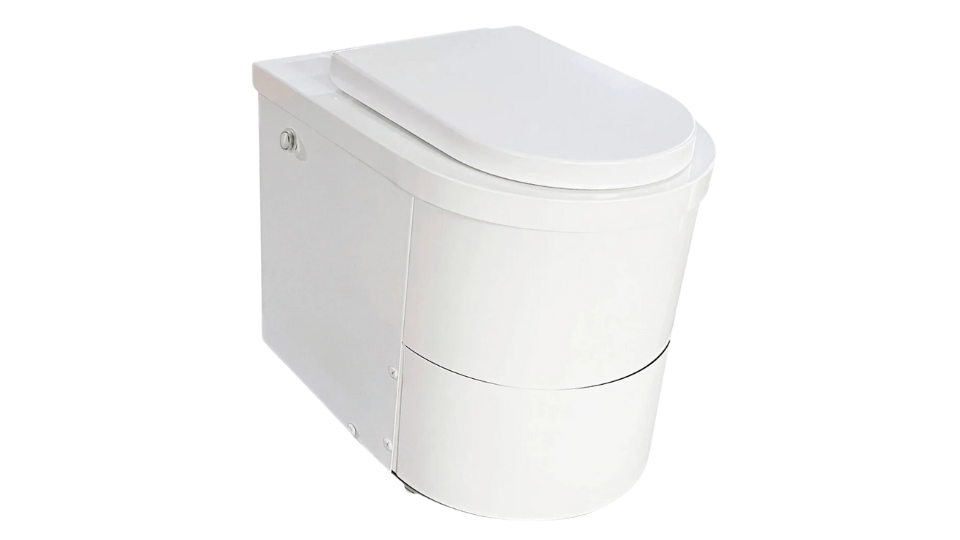

How Incinerating Toilets Work?
Ecojohn’s incinerating toilets are designed for simplicity and efficiency. These systems operate:
- Waste Collection:After use, the waste is collected in a bowl that is often lined with bowl liners. These liners help keep the incinerating chamber clean and make the maintenance process easier.
- Incineration Process: Once the waste is collected, the user starts the incineration process. The waste is transferred to the chamber, where it is subjected to extremely high temperatures. Depending on the model, the heat is generated by electricity, natural gas, propane, or diesel. The burn cycle can vary in duration, but it is designed to completely incinerate the waste, leaving behind only sterile ashes.
- Ash Disposal:After the incineration process is complete, the remaining sterile ash—usually about a tablespoon per use—is collected in a tray. The ash can be safely disposed of in the trash or even used as a soil additive in a garden, though it doesn’t have the same nutrient value as compost from a composting toilet.

Energy Consumption
The consumption of energy from Ecojohn incinerating toilets is a critical consideration. These systems require a power source to achieve the necessary incineration temperatures. Electric models draw a certain number of kilowatt hours during each burn cycle, while gas-powered versions consume natural gas, propane, or diesel.
Ecojohn’s designs are optimized for efficiency, with features such as automatic shut-off and insulated incineration chambers to conserve energy. While the power consumption may be higher than that of a traditional composting toilet, the trade-off is a cleaner and more convenient waste management solution.
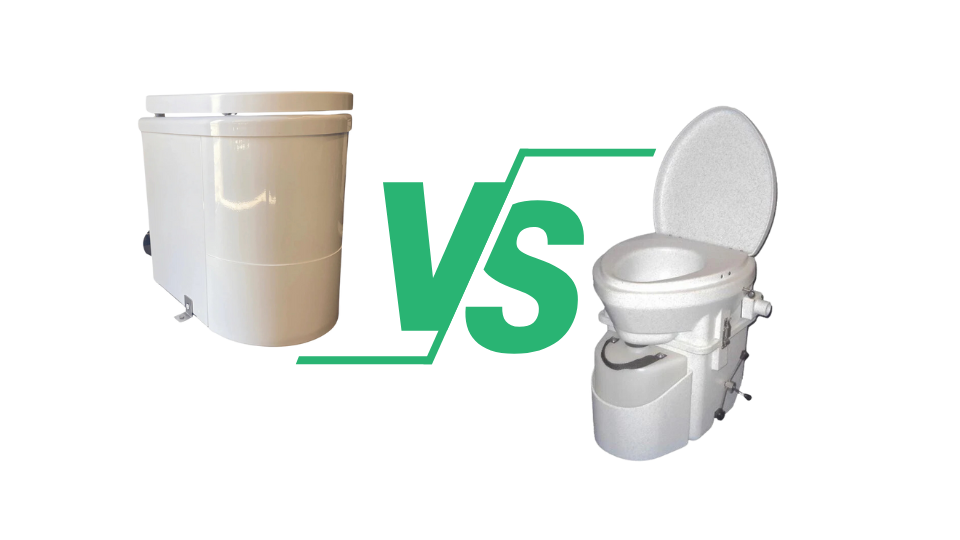
The Ecojohn vs. Composting Toilets
Key differences between Ecojohn and composting toilets include the following:
- Waste Treatment:The primary difference between incinerating toilets and composting toilets lies in their approach to waste treatment. Incinerating toilets burn waste and convert it into sterile ashes while composting toilets decompose waste into compost over time.
- Environmental Impact: Incinerating toilets are highly efficient in water usage, requiring no water to operate. In contrast, composting toilets produce compost that can benefit gardening but may need more space and careful management to avoid issues like odors or pests.
- Suitability for Different Environments: Incinerating toilets are ideal for environments where water is scarce or where mobility is a priority, such as in RVs or tiny homes. Composting toilets are better suited for stationary environments where the composting process can be carefully monitored and managed.
- Cost and Maintenance: Incinerating toilets tend to have higher upfront costs due to the technology involved. However, they require less ongoing maintenance compared to composting toilets, which need regular management of the composting material and periodic emptying of the composting chamber.

Advantages and Limitations of Incineration Toilet
Advantages
- Hygiene and Sanitation: Incinerating toilets offer superior sanitation by completely destroying waste reducing the risk of pathogens and unpleasant odors.
- Space Efficiency:These systems are perfect for small living spaces, such as tiny homes or RVs, where traditional plumbing might not be feasible.
- Minimal Water Usage:The waterless operation of incinerating toilets conserves water, making them an excellent option for areas with limited water supply.
Limitations
- Energy Dependence: Incinerating toilets require an external power source—whether electricity, propane, or diesel—to function, which can be a limitation in areas without reliable access to power.
- Initial Cost: The initial cost of purchasing and installing an incinerating toilet is generally higher than other off-grid options, such as composting toilets.
Practical Considerations for Choosing an Incinerator Toilet
Installation Requirements
When installing an Ecojohn incinerating toilet, several factors need to be considered. The installation site must have enough space to accommodate the toilet and incineration chamber. Proper ventilation is also essential to safely expel the exhaust gases produced during the burn cycle. Finally, access to a reliable power source— electricity or fuel-based—is necessary for the toilet’s operation.

Legal and Regulatory Concerns
Before installing an incineration toilet, it’s essential to check local regulations. Some areas have specific rules regarding the installation and operation of incinerating toilets, particularly concerning emissions and the disposal of sterile ashes.
Maintenance Tips
Maintaining an incineration toilet is a relatively low effort but essential for long-term functionality. Regular checks on the incineration chamber for residue buildup, ensuring the ventilation system is clear, and periodic emptying of the ash tray is vital. Following these maintenance tips will help ensure the system remains efficient and reliable.
Conclusion
Incinerating toilets, particularly those from Ecojohn, offer a compelling solution for off-grid sanitation. These toilets provide a unique combination of hygiene, water conservation, and space efficiency, making them ideal for remote locations, mobile homes, and eco-conscious individuals.
However, it’s essential to balance the benefits against the limitations, especially in terms of energy consumption and initial cost. By carefully considering your specific needs, environment, and preferences, you can make an informed decision about whether an incinerating toilet is the right choice for you.

Have any questions or would like to place an order? We'd love to help! Chat with our friendly customer service team by calling 1-844-945-3625, chatting in on our website or email us at customersupport@wildoaktrail.com. We look forward to hearing from you!
Leave a comment
Comments will be approved before showing up.